Mixed probiotic/anti-mycotoxin additive (Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007) supplementation of AFB1-contaminated feed influences broiler chickens productive parameters, biochemistry and liver/intestine histopathology
Keywords:
broiler chickens, probiotic, antibiotic, aflatoxin B1, growth performance.Abstract
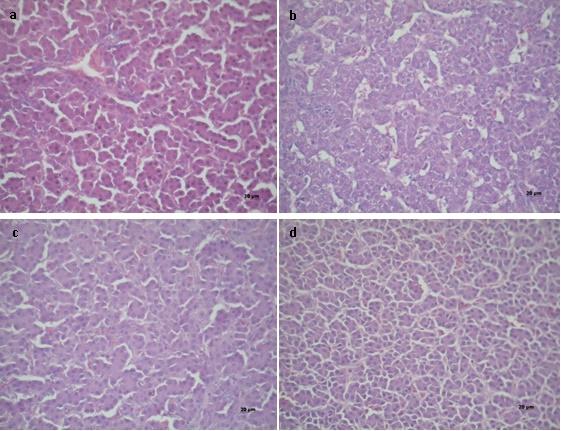
The objective of the present work was to study the influence of dietary supplementation of a probiotic and anti-mycotoxin mixed additive (MA, Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007) and their interaction on the performance and health (biochemistry and livers/intestines histopathology) of broiler chickens fed aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) contaminated diets. A total of 60 one-day-old Cobb broilers were randomly allocated into four treatment groups with three replicates of 5 birds each for a five-week d feeding experiment. The dietary experimental of each treatment (T) were formulated as follows: T1, a commercial diet (CD); T2, CD + AFB1 (506.14 ± 22.1 ng/kg); T3, CD + 0.1% MA, the ratio of S. cerevisiae RC016 (1 x 107 cells/g) to L. rhamnosus RC007 (1 x 108 cells/g) was 1:1; T4, CD + AFB1 (506.14 ± 22.1 ng/kg) + 0.1% MA. The MA improved (p<0.01) production parameters (weight gain, conversion rate, and carcass yield) and reduced (p < 0.01) the toxic effect of AFB1 on the relative weight of the livers. In addition, the macro and microscopic alterations of livers and the possible intestinal injury related to histological damage in the presence of mycotoxin were reduced. The use of probiotic MA based on S. cerevisiae RC016 and L. rhamnosus RC007 in animal feed provides greater protection against mycotoxin contamination and is safe for use as a supplement in animal feed, exercising benefit effects that improve animal health and productivity. This is of great importance at the economic level for the avian production system.
Downloads
References
Abd El-Moneim, A. E. M. E.; El-Wardany, I.; Abu-Taleb, A. M.; Wakwak, M. M.; Ebeid, T. A.; Saleh, A. A. 2020 Assessment of in ovo administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium longum on performance, ileal histomorphometry, blood hematological, and biochemical parameters of broiler chickens. Probiotics and antimicrobial proteins. 12(2):439-450.
Akinrinmade, F.J.; Akinrinde, A.S.; Amid, A. 2016. Changes in serum cytokine levels, hepatic and intestinal morphology in aflatoxin B.-induced injury: modulatory roles of melatonin and flavonoid-rich fractions from Chromolena odorata. Mycotoxin Research. 32:53-60.
Alagawany, M.; El-Hack, M.E.A.; Farag, M.R.; Sachan, S.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K. 2018. The use of probiotics as eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in poultry nutrition. Environmental Science Pollution Research. 25:10611-10618.
Alonso, V.A.; Monge, M.P.; Larriestra, A.; Dalcero, A.M.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Chiacchiera, S.M. 2010. Naturally occurring aflatoxin M. in raw bulk milk from farm cooling tanks in Argentina. Food Additives Contaminants. 27:373-379.
Arif, M.; Iram, A.; Bhutta, M. A.; Naiel, M. A.; El-Hack, A.; Mohamed, E.; Taha, A. E. 2020. The biodegradation role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae against harmful effects of mycotoxin contaminated diets on broiler chicken’s performance, immunity status, and carcass characteristics. Animals. 10(2): 238.
Armando, M.R.; Dogi, C.A.; Rosa, C.A.; Dalcero, A.M.; Cavaglieri, L.R. 2012. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and the reduction of Aspergillus parasiticus growth and aflatoxin B. production at different interacting environmental conditions, in vitro. Food Additives and Contaminants. 29:1443-1449.
Bai, S.P.; Wu, A.M.; Ding, X.M.; Lei, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, K.Y.; Chio, J.S. 2013. Effects of probiotic-supplemented diets on growth performance and intestinal immune characteristics of broiler chickens. Poultry Science. 92:663-670.
Blajman, J.; Gaziano, C.; Zbrun, M.V.; Soto, L.; Astesana, D.; Berisvil, A.; Frizzo, L. 2015. In vitro and in vivo screening of native lactic acid bacteria toward their selection as a probiotic in broiler chickens. Research in Veterinary Science. 101:50-56.
Caly, D.L.; D'Inca, R.; Auclair, E.; Drider, D. 2015. Alternatives to antibiotics to prevent necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens: a microbiologist's perspective. Frontiers Microbiology. 6:1336.
Chiocchetti, G.M.; Jadán-Piedra, C.; Monedero, V.; Zúñiga, M.; Vélez, D.; Devesa, V. 2019. Use of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts to reduce exposure to chemical food contaminants and toxicity. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 59:1534-1545.
Dale, N. 1994. National research council nutrient requirements of poultry–ninth revised edition. Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 3(1):101.
Del Carmen, S.; Zurita-Turk, M.; Lima, F.A.; Dos Santos, J.C.; Leclercq, S.Y.; Chatel, J.M.; LeBlanc, J.G. 2013. A novel interleukin-10 DNA mucosal delivery system attenuates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model. European Journal of Inflammation. 11:641-654.
Dogi, C.A.; Fochesato, A.; Armando, R.; Pribull, B.; Souza, M.M.S.; da Silva Coelho, I.; Cavaglieri, L. 2013. Selection of lactic acid bacteria to promote an efficient silage fermentation capable of inhibiting the activity of Aspergillus parasiticus and Fusarium gramineraum and mycotoxin production. Journal Applied Microbiology. 114:1650-1660.
FAO/WHO. 2001 Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food including Powder Milk.
Fochesato, A.S.; Galvagno, M.A.; Cerrutti, P.C.; Gonzalez Pereyra, M.L. 2018. Optimization and Production of Probiotic and Anti-mycotoxin Yeast Biomass Using Bioethanol Industry Waste via Response Surface Methodology. Advanced Biotech Microbiology. 81:555727.
Gadde, U.; Kim, W.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lillehoj, H.S. 2017. Alternatives to antibiotics for maximizing growth performance and feed efficiency in poultry: a review. Animal Health Research Reviews. 18:26-45.
García, G.R.; Payros, D.; Pinton, P.; Dogi, C.A.; Laffitte, J.; Neves, M.; Oswald, I.P. 2017. Intestinal toxicity of deoxynivalenol is limited by Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007 in pig jejunum explants. Archives of Toxicology. 92:983-993.
Gonzalez Pereyra, M.; Dogi, C.; Torres Lisa, A.; Wittouck, P.; Ortiz, M.; Escobar, F.; Bagnis, G.; Yaciuk, R.; Poloni, L.; Torres, A.; Dalcero, A.; Cavaglieri, L. 2014. Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity evaluation of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016: a 60-day subchronic oral toxicity study in rats. Journal Applied Microbiology. 117(3):824-33.
Hasan, S.; Hossain, M.M.; Alam, J.; Bhuiyan, M.E.R. 2015. Beneficial effects of probiotic on growth performance and hemato-biochemical parameters in broilers during heat stress. International Journal Innovation and Applied Studies. 10:244.
Hornbuckle W.E.; Tennant B.C. 2008. Hepatic Function. Chapter. 15 - Gastrointestinal Function, Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animal. 413-457.
Liew, W.P.P.; Mohd-Redzwan, S. 2018. Mycotoxin: its impact on gut health and microbiota. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 8:60.
Magnoli, A.P.; Monge, M.P.; Miazzo, R.D.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Magnoli, C.E.; Merkis, C.I.; Cristofolini, A.L.; Dalcero, A.M.; Chiacchiera, S.M. 2011. Effect of low levels of aflatoxin B. on performance, biochemical parameters, and aflatoxin B. in broiler liver tissues in the presence of monensin and sodium bentonite. Poultry Science. 90:48–58.
Magnoli, A.P.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Pereyra, M.G.; Poloni, V.L.; Peralta, M.F.; Nilson, A.J.; Cavaglieri, L.R. 2017. Use of yeast (Pichia kudriavzevii) as a novel feed additive to ameliorate the effects of aflatoxin B. on broiler chicken performance. Mycotoxin Research. 33:273-283.
Mehdi, Y.; Létourneau-Montminy, M.P.; Gaucher, M.L.; Chorfi, Y.; Suresh, G.; Rouissi, T.; Godbout, S. 2018. Use of antibiotics in broiler production: Global impacts and alternatives. Animal Nutrition. 4:170-178.
Mutlu, A.G.; Kursun, O.; Kasİmoglu, A.; Dukel, M. 2010. Determination of aflatoxin M. levels and antibiotic residues in the traditional Turkish desserts and ice creams consumed in Burdur city center. Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advanced. 9:2035-2037.
Ortatatli, M.; Oguz, H.; Hatipoglu, F.; Karaman, M.X. 2005. Evaluation of pathological changes in broilers during chronic aflatoxin (50 and 100 ppb) and clinoptilolite exposure. Research Veterinary Science. 78:61-68.
Park, S.H.; Lee, S.I.; Ricke, S.C. 2016. Microbial populations in naked neck chicken ceca raised on pasture flock fed with commercial yeast cell wall prebiotics via an Illumina MiSeq platform. PLoS One. 11(3): e0151944.
Peng, Q.Y.; Li, J.D.; Li, Z.; Duan, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.P. 2016. Effects of dietary supplementation with oregano essential oil on growth performance, carcass traits and jejunal morphology in broiler chickens. Animal Feed Science and Technology. 214:148-153.
Pizzolitto, R.P.; Salvano, M.A.; Dalcero, A.M. 2012. Analysis of fumonisin B. removal by microorganisms in co-occurrence with aflatoxin B. and the nature of the binding process. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 156:214-221.
Pizzolitto, R.P.; Armando, M.R.; Salvano, M.A.; Dalcero, A.M.; Rosa, C.A. 2013. Evaluation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as an antiaflatoxicogenic agent in broiler feedstuffs. Poultry Science. 92:1655-1663.
Poloni, V.; Magnoli, A.; Fochesato, A.; Cristofolini, A.; Caverzan, M.; Merkis, C.; Cavaglieri, L. 2020. Saccharomyces cerevisiae RC016-based feed additive reduces liver toxicity, residual aflatoxin B. levels and positively influences intestinal structure in broiler chickens fed on chronic aflatoxin B. levels-contaminated diets. Animal Nutrition. 6:31-38.
Ronquillo, M.G.; Hernandez, J.C.A. 2017. Antibiotic and synthetic growth promoters in animal diets: review of impact and analytical methods. Food Control. 72:255-267.
Śliżewska, K.; Cukrowska, B.; Smulikowska, S.; Cielecka-Kuszyk, J. 2019. The effect of probiotic supplementation on performance and the histopathological changes in liver and kidneys in broiler chickens fed diets with aflatoxin B1. Toxins. 11:112.
Trucksess, M.W.; Stack, M.E.; Nesheim, S.; Albert, R.; Romer, T. 1994. Multifunctional column coupled with liquid chromatography for determination of aflatoxins B., B., G. and G. in corn, almonds. Brazil nuts, peanuts, and pistachio nuts: Collaborative study. Journal AOAC International. 77:1512-1521.
Vuong, C.N.; Chou, W.K.; Hargis, B.M.; Berghman, L.R.; Bielke, L.R. 2016. Role of probiotics on immune function and their relationship to antibiotic growth promoters in poultry, a brief review. International Journal of Probiotics and Prebiotics. 11:1-7.
Fochesato, A.S.; Cuello, D.; Poloni, V.; Galvagno, M.A.; Dogi, C.A.; Cavaglieri, L.R. 2019. Aflatoxin B1 adsorption/desorption dynamics in the presence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus RC007 in a gastrointestinal tract‐simulated model. Journal Applied Microbiology. 126:223-229.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ab Intus

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

















